Deep Learning is the study of neural network that are networks of neurons that are the fundamental unit of computation.
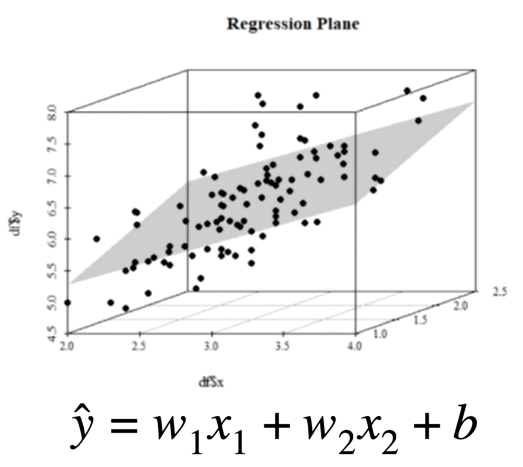
From the multiple linear regression above, we converted the beta coefficients in weights w1, w2 and they are essentially the slope for each of the individual inputs x1 and x2. Another way to think of the weights is that thay tell us how important each input to predict the output.
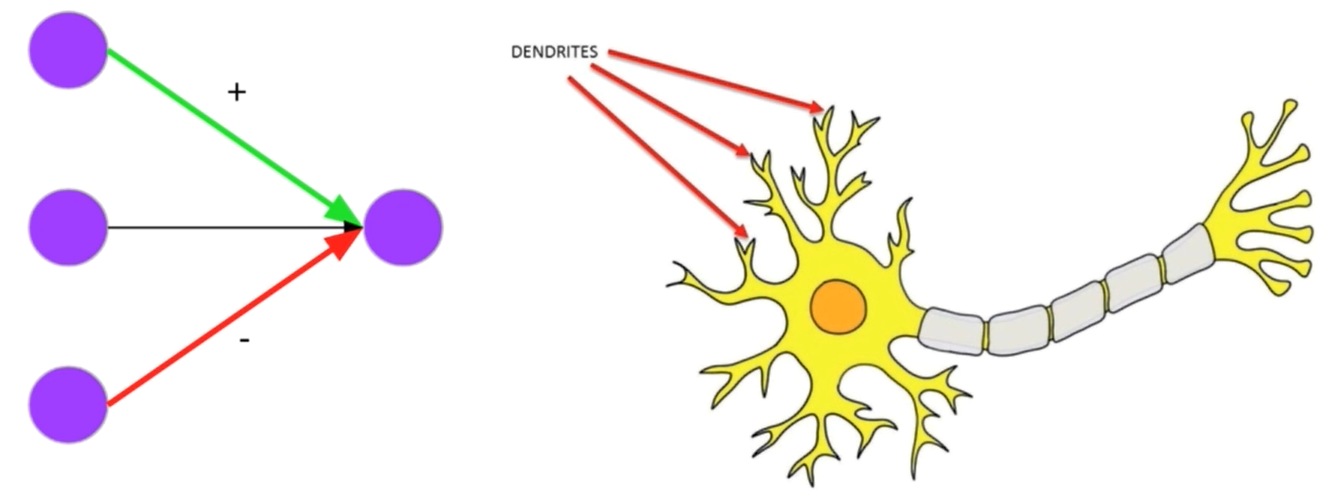
In fact, the left figure above shows us three input neurons where the first in green has a large positive impact on the activation, the second neuron has less impact, and the third in red has large negative impact; exactely the same of the relative importance weights that we use to find the most important independent variables in a multiple regression. This could be related to neurons where the dendrites are our inputs. Fr example when our eyes see something an electrical signal goes alonf the nerves in out eyes and travel to the brain. The same is when we hear or smell something or touch something. Now, the neuron has to decide if it is going to pass this signal on to outgoing neurons. The neuron do that in a very simila way to the linear and logistic regression: it sums up all the incoming signals and this summation becomes the outgoing signal. Some input connections are strong but others are weak. Moreover, some connections exite the receiving neuron while other connections inhibit the receiving neurons: this is just like the weights of a regressino model.
Action Potential The signal that gets passed along the neurons has a special name: active potential: basically it is a spike in electrical potential. If we measure the electrical potential over time at a particular pointin the neuron we would see a signal as shown in the figure below.
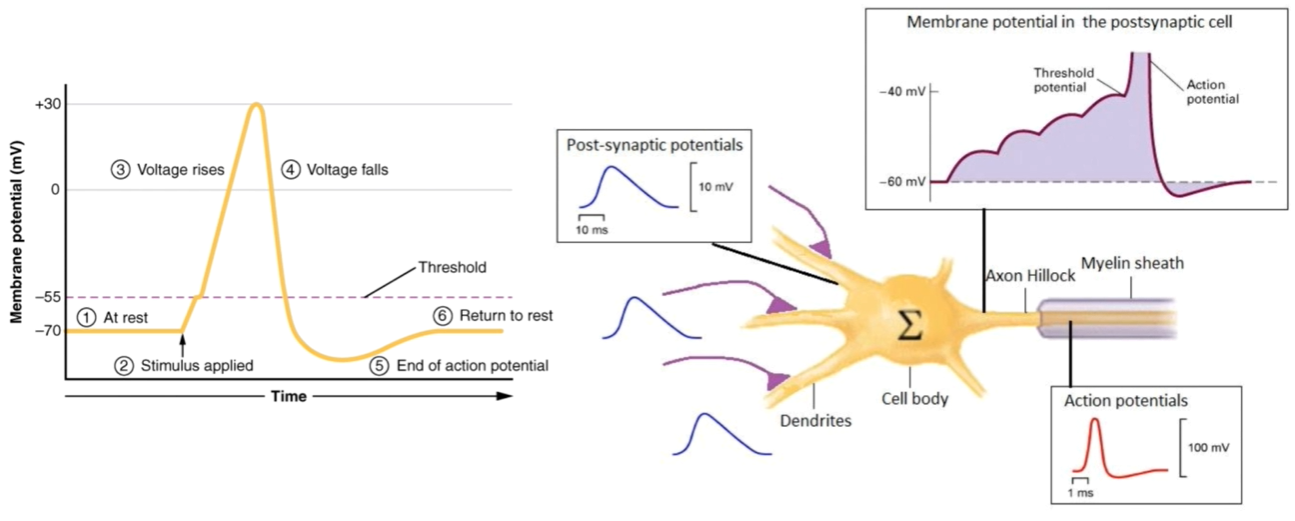
The neuron is more like a logistic regression than a linear regression. Basically we are going to sum up all the influences from all the incoming neurons, and if the electrical potential of the sum is grater than some threshold, then an action potential will propagate through the receiving neuron. This is like a binary classificatiion where we make prediction of 0 and 1, and in biology that is called All or None Principle.
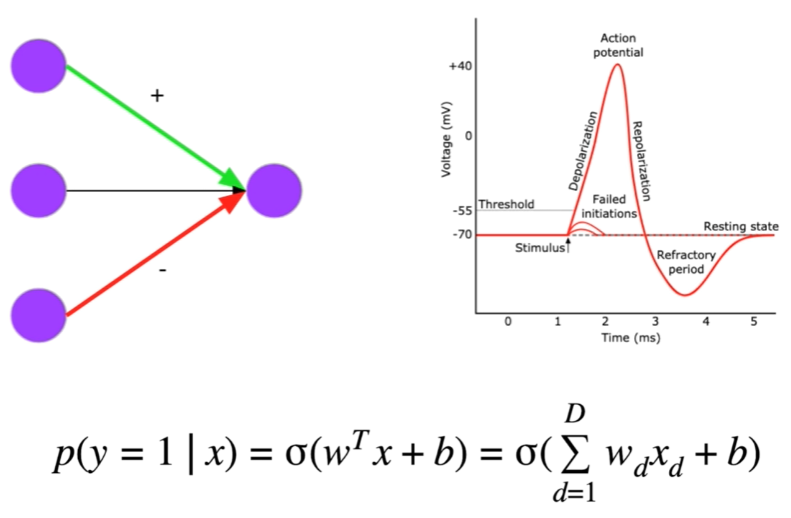
Each xi represent the inputs, and w is a weight that tells us how strong is the connection with xi in a positive or negative influence of the activation potential. The weighted sum of each xi is then added to the bias ter or threshold and then passed to the sigmoind function taht tell us wheter or not an action potential should occur.