Introduction A fascinating aspect of our brain is the Synaptic pruning. One of the grand strategies nature uses to construct nervous systems is to overproduce neural elements, such as neurons, axons and synapses, and then prune the excess. In fact, this overproduction is so substantial that only about half of the neurons mammalian embryos generate will survive until birth. At the same way the pruning in ANN is used to eliminate redundant connections between neurons during the training. This process is also known as Drop-out and play an essential role in Back Propagation.
Alpha Beta Pruning The idea is to find the minimax of a game tree. It is a technique by which without checking each node of the game tree we can compute the correct minimax decision, and this technique is called pruning. This involves two threshold parameter Alpha and Beta for future expansion, so it is called alpha-beta pruning. Alpha: is the best (highest-value) choice we have found so far at any point along the path of Maximizer. The initial value of alpha is -∞. Beta: The best (lowest-value) choice we have found so far at any point along the path of Minimizer. The initial value of beta is +∞.
The Alpha-beta pruning removes all the nodes which are not really affecting the final decision but making algorithm slow. Hence by pruning these nodes, it makes the algorithm fast.
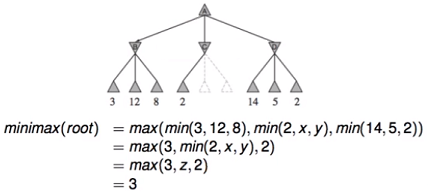
We have an example on the figure above. If we do minimax at the root level A, this would be the maximum of the nodes B, C, D, and each of these nodes have to be the minimum of their values below the tree. The result is 3, and we do not need z. We do not need z which is the min(2,x,y) because z <= 2, and so the max(3,z,2) is 3, and we do not need to explore the others two nodes of C (x,y).
In the Alpha-beta pruning the Alpha is the value of best choice so far fot MAX (highest value), and Beta is the value of bets choice so far for MIN (lowest value). Each node keep track of its Alpha and Beta values.
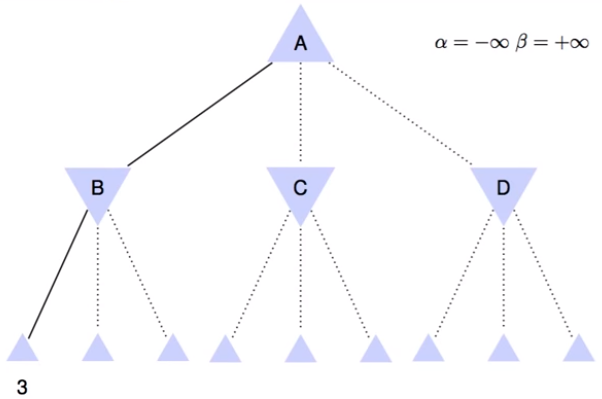
We start with Alpha = -∞, Beta = +∞, and we want to increase the Alpha value but also Alpha has to be less or euqal to Beta. In the previous example, we had as first value 3, and now we have to ask if 3 is less than Alpha (-∞). Becasue 3 is greater than Alpha, and less than Beta (+∞), we can update Beta = 3. We continue this process for all the values in the tree.
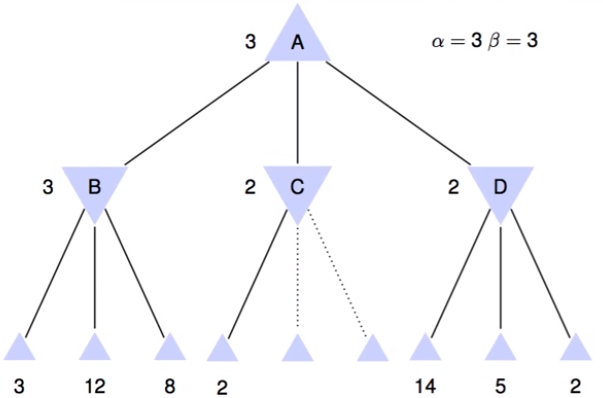
At the end of the algorithm the minimax for the root node A is 3, and we did not explore the two not defined final nodes of C. Moreover, if we reorder the final nodes of D by 2,5,14 we immediately discover the solution for this node which is 2. Crucially, when we have to deal with a large number od nodes, this procedure save us a lot of time, and we arrive faster to the solution without affecting the final outcome. This procedure is called metareasoning.