It is a Probability Classifier. Naïve Bayes is the first algorithm that should be considered for solving Text Classification Problem which involves High Dimensional training Dataset. A few examples are: Sentiment Analysis and Classifying Topics on Social Media. It also refers to the Bayes’ Theorem also known as Bayes’ Law that give us a method to calculate the Conditional Probability: that is the probability of an event, based on previous knowledge available on the events.
Consider for example to have two features: Salary and Age. Some Walks to go at work and other Drive at work.
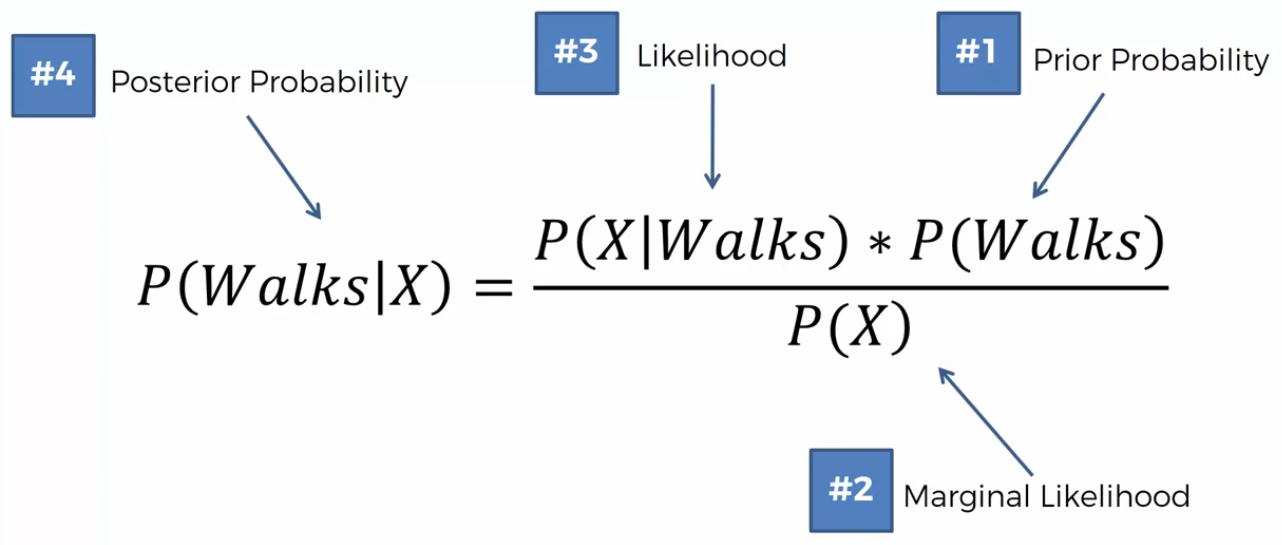
\[ P(W a l k s | X)=\frac{P(X | \text { Walks }) * P(\text { Walks })}{P(X)} \]
The X represent the features (Salary or Age) of a specific person.
What is the probability that the person goes to work on foot based on X (Salary and Age)? P(Walks) = Prior probability, P(X) = Marginal likelihood, P(X|Walks) = Likelihood. The result of this calculation is P(Walks|X) = Posterior probability. Now, the same have to be made for Drive.
Finally, we have to compare P(Walks|X) vs. P(Drives|X), and from there we can decide in which class we have to put our new observatioin.
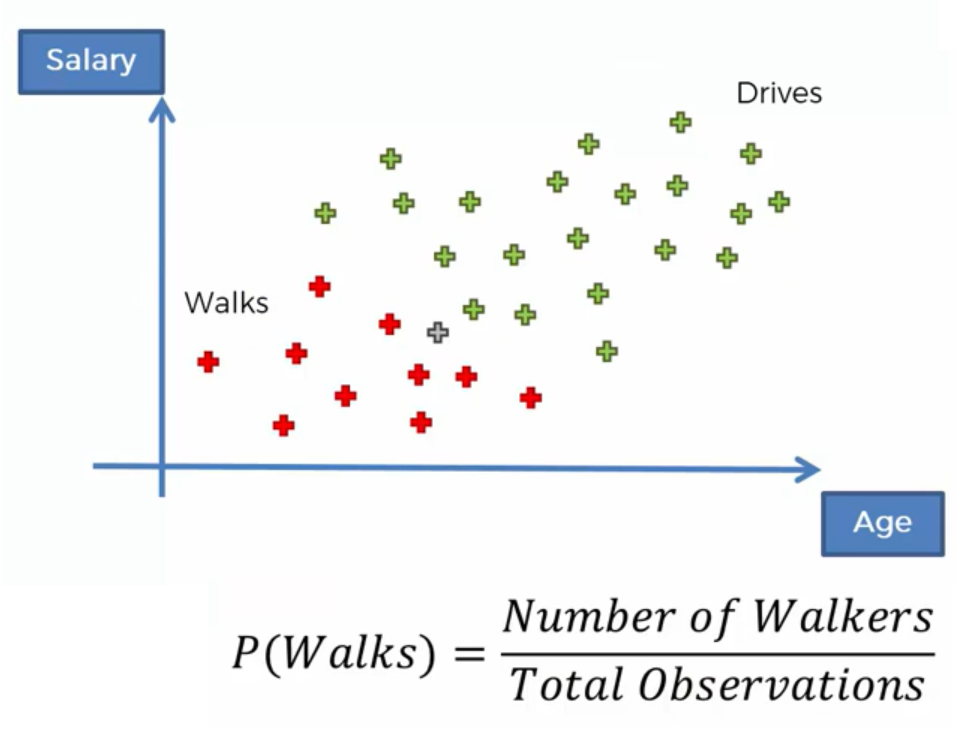
Prior Probability In our example is the Probability that somebody Walks at work without knowing about hisAge or Salary. Looking at the figure below, we have to calculate the number of red observations and devide it by the overall number.
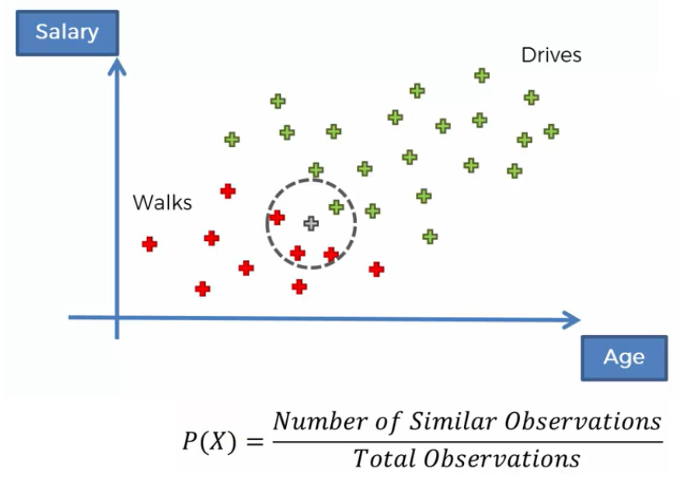
Marginal Likelihood We select a circle around our point (person) that we have to estimate. Then, we calculate the probability of Similar Features (walks, drives) that this person has with the other observations (person). So, Marginal Likelihood says to us what is the likelihood of any new random variable that we have fully inside the circle that we defined.
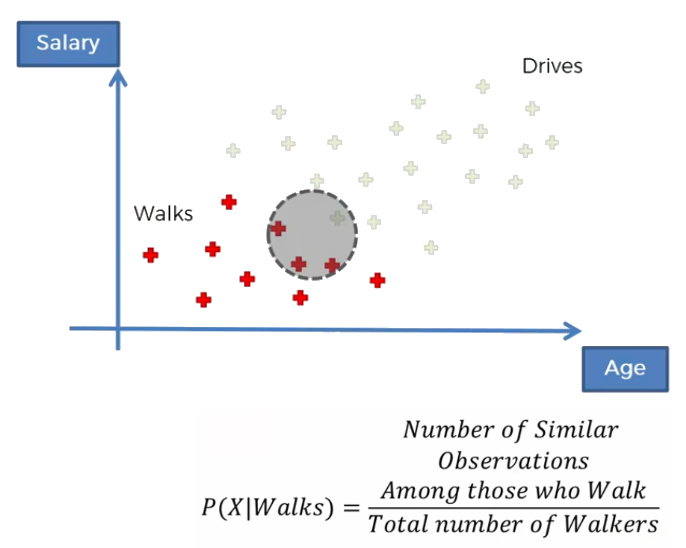
Likelihood It answer the following question: what is the probability of a randomly selected observations to be similar to the observations that we selected by the circle? In our example, this means that we take into consideration only the red points (i.e. people that work at work). We are asking what is the likelihood that a randomly selected data point is someone that exhibit features similar to the people selected in the random circle.
Naive Bayes in Machine Learning In a Machine Learning classification problem where there are multiple features and classes, the aim of the Naïve Bayes is to calculate the conditional probability of an object with the feature vector x1, x2, xn. So, it is able to calculate the probability of a particular class Ci given N number of features. Naive Bayes is an effective and commonly-used, machine learning classifier. It is a probabilistic classifier that makes classifications using the Maximum A Posteriori decision rule in a Bayesian setting. It can also be represented using a very simple Bayesian network. Naive Bayes classifiers have been especially popular for text classification, and are a traditional solution for problems such as Spam Detection.
An intuitive explanation for the Maximum A Posteriori Probability MAP is to think probabilities as degrees of belief. For example, how likely are we vote for a candidate depends on our prior belief. We can modify our stand based on the evidence. Our final decision, based on evidence, is the posterior belief, which is what happens after we sifted through the evidence. MPA is simply the maximum posterior belief: after going through all the debates, what is your most likely decision?